An architectural pattern may be a general, reusable answer to a commonly occurring downside in software architecture in a given context. Architectural patterns are similar to software design patterns, but they have a broader scope. Architectural patterns address varied problems in software engineering, like hardware performance limitations, high accessibility, and business risk minimization. Some architectural patterns are enforced among software frameworks.
Table of Content
- Interpreter Architectural pattern
- Blackboard Architectural pattern
- Model-view-controller Architectural pattern
- Layered Architectural pattern
- Client-server Architectural pattern
- Master-slave Architectural pattern
- Pipe-filter Architectural pattern
- Broker Architectural pattern
- Peer-to-peer Architectural pattern
- Event-bus Architectural pattern
10 Comparison of Architectural Patterns with advantages and disadvantages
1. Interpreter Architectural pattern
 |
Interpreter pattern |
This pattern is utilized to design an element that interprets programs written in a very dedicated language. It mainly specifies the way to measure lines of programs, called sentences or expressions, written during a specific speech. The essential plan is to possess a category for every symbol of the word.
- Database query languages like SQL.
- Languages won't describe communication protocols.
- Highly dynamic behavior is feasible.
- Suitable for end-user programmability.
- Enhances flexibility, as a result of commutation, an understood program is straightforward
- Because an interpreted language is usually slower than a compiled one, performance could also be a problem.
2. Blackboard Architectural pattern
 |
Blackboard pattern |
This pattern is helpful for issues that no settled resolution methods are illustrious. The blackboard pattern consists of three main elements.
- Blackboard — a structured world memory containing objects from the answer area
- Control element — selects, configures, and executes modules.
- Knowledge source — specialised modules with their own illustration
All the elements have access to the blackboard. Elements could create new information objects that are unique to the blackboard. Elements seek specific information styles on the blackboard and will notice these by pattern matching with the present data source.
- Speech recognition
- Protein structure identification
- Vehicle identification and trailing
- Sonar signals interpretation.
- Easy to feature new applications.
- Extending the structure of the info area is straightforward.
- Modifying the structure of the info space is challenging, as all applications are affected.
- It may need synchronization and access management.
3. Model-view-controller Architectural pattern
 |
Model-view-controller pattern |
- Model — contains the core practicality and knowledge
- View — displays the data to the user (more than one read is also defined)
- Controller — handles the input from the user
Usage
- Architecture for World Wide Internet applications in major programming languages.
- Web frameworks like Django and Rails.
- Makes it simple to own multiple views of the constant model, which may be connected and disconnected at run-time.
- Increases complexness.
- It might result in several additional updates for user actions.
4. Layered Architectural pattern
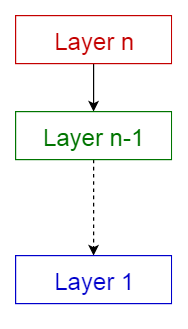 |
Layered pattern |
This pattern is additionally called the n-tier architecture pattern. It is wont to structure programs that may be rotten into teams of subtasks, every one of which is at a selected level of abstraction. Every layer provides services to the subsequent higher layer.
The four most customarily found layers of a general data system are as follows.
- The presentation layer (also called the UI layer)
- Application layer (also called service layer)
- The business logic layer (also called the domain layer)
- The data access layer (also called the persistence layer)
Usage
- General desktop applications.
- E-commerce net applications.
Advantages
- A lower layer is used by entirely different higher layers.
- Layers make standardization easier as we will clearly outline levels.
- Changes are created among the layers while not moving different layers.
Disadvantages
- Not universally applicable.
- Specific layers could be skipped for certain things.
- See this: Android Oreo cookie Vs. iOS eleven: Comparison. You must comprehend this.
5. Client-server Architectural pattern
 |
Client-server pattern |
This pattern consists of 2 parties; a server and multiple purchasers. The server part can give services to various shopper parts. Purchasers request services from the server, so the server provides relevant services to those purchasers. What is more, the server continues to pay attention to client requests.
Usage
- Online applications like email, document sharing, and banking.
Advantages
- Kindly model a group of services wherever clients request them.
Disadvantages
- Requests are usually handled in separate threads on the server.
- Inter-process communication causes overhead as entirely different clients have different representations.
- Recommended : Comparison: Android O vs. Android N
6. Master-slave Architectural pattern
 |
Client-server pattern |
This pattern consists of 2 parties; master and slaves. The master part distributes the work among identical slave parts and computes an end result from the results that the slaves return.
Usage
- In information replication, the master information is considered the reliable supply, and therefore the slave databases are synchronized to it.
- Peripherals connected to a bus during a computing system (master and slave drives).
Advantages
- Accuracy – The execution of a service is delegated to entirely different slaves, with completely different implementations.
Disadvantages
- The slave's area unit is isolated: there's no shared state.
- For example, the latency within the master-slave communication is a problem in period systems.
- This pattern will solely be applied to a tangle that may be rotten you recognize: issues with Android Oreo cookie – 6 belongings you got to know.
Best Android Course: Android Course online 2024
7. Pipe-filter Architectural pattern
 |
Pipe-filter pattern |
This pattern is wont to structure systems that manufacture and method a stream of information. Every process step is boxed among a filter component. Information to be processed is tried and right pipes. These pipes are used for buffering or for synchronisation functions.
Usage
- Compilers. The following filters perform lexical analysis, parsing, linguistic analysis, and code generation.
- Workflows in bioinformatics.
Advantages
- Exhibits synchronic process. Once input and output carry with their streams, filters begin computing once they receive information.
- Easy to feature filters. The system is extended merely.
- Filters area unit reusable. Will build completely different pipelines by recombining a given set of filters
Disadvantages
- Efficiency is prescribed by the slowest filter method.
- Data transformation overhead once moving from one filter to a different one.
8. Broker Architectural pattern
 |
Broker pattern |
This pattern is employed to structure distributed systems with decoupled parts. These parts will act with one another through remote service invocations. A broker element is responsible for coordinating communication among components.
Servers publish their capabilities (services and characteristics) to a broker. When clients request assistance from the broker, the broker redirects them to an acceptable service from its written account.
Usage
- Message broker software systems like Apache ActiveMQ, Apache Kafka, RabbitMQ, and JBoss electronic communication.
Advantages
- It allows dynamic modification, addition, deletion, and relocation of objects and makes distribution clear to the developer.
Disadvantages
- Requires standardization of service descriptions.
- See this additionally: See What’s New in an android oreo cookie
9. Peer-to-peer Architectural pattern
 |
Peer-to-peer pattern |
In this pattern, individual parts are called peers. Peers could perform each as a client, requesting services from different peers, or as a server, providing services to different peers. A peer could act as a shopper, a server, or each, and it will modify its role dynamically with time.
Usage
- File-sharing networks like Gnutella and G2)
- Multimedia protocols like P2PTV and PDTP.
- Proprietary transmission applications like Spotify.
Advantages
- Supports redistributed computing.
- Highly robust within the failure of any given node.
- Highly scalable regarding resources and computing power.
Disadvantages
- There is no guarantee regarding the quality of service, as nodes join forces voluntarily.
- Security is tight to be secure.
- Performance depends on the number of nodes.
10. Event-bus Architectural pattern
 |
Event-bus pattern |
This pattern may primarily deal with events and has four major components: event supply, event attendee, channel, and event bus. Sources publish messages to specific channels on a happening bus. Listeners subscribe to particular channels. Listeners are notified of messages that the area unit revealed to a pathway that they need to be signed before.
Usage
- Android development
- Notification services
Advantages
- New publishers, subscribers, and connections are extra simple.
- Useful for highly distributed applications.
Disadvantages
- Scalability is also a tangle, as all messages travel through an equivalent event bus.











